TEP Essentials
Content
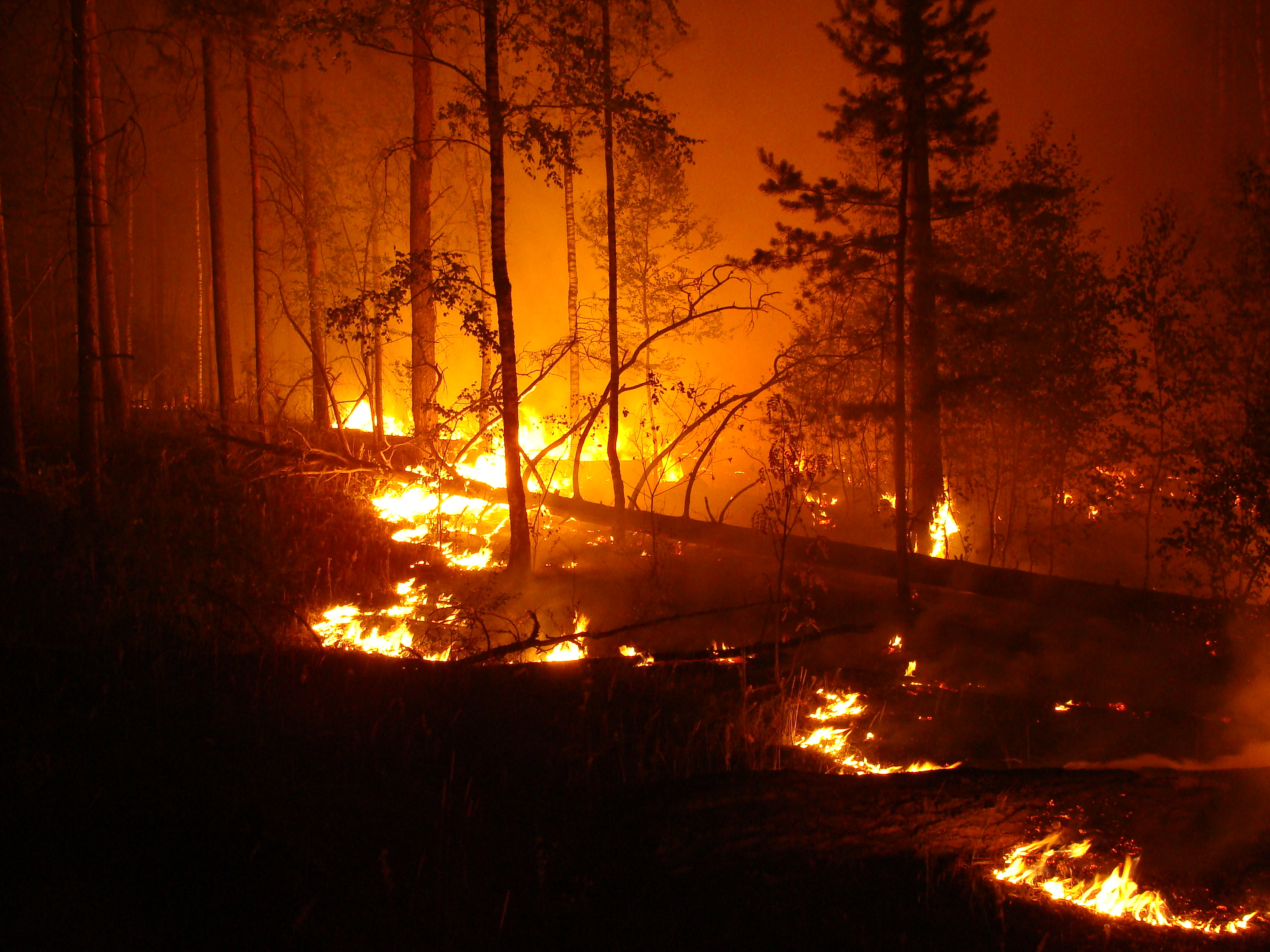
C1: Fire Behaviour Fundamentals
1. Introduction.
1.1 Generations of wildfires.
- Description of wildfire generations as a concept to help understand their evolution.
2. Fire behaviour fundamentals.
2.1. Wildfire spread factors. The fire triangle and heat transfer
mechanisms.
- The fire triangle, fuel, oxidising agent, heat, the chain reaction and its relation to
suppression methods: suffocation, elimination of fuel, cooling. Forms of heat transfer:
conduction, radiation, convection. Rolling materials, embers and secondary spot fire
ignitions.
2.2. Fire behaviour variables and their changes in wildfire development
- Fire behaviour variables: flame length, rate of spread and secondary spot fires. Relation
between the variables and our suppression capacity.
2.3. The parts of a wildfire and their connection with spread factors and
behavioural variables
- Parts of a wildfire (flanks, head, tail) and the spread axis. Denomination by cardinal points
and grid method.
2.4. The wildfire behaviour triangle, introduction to spread patterns
- The fire behaviour triangle: meteorology, fuel and topography. Introducing what the
wildfire wants to do: spread pattern.
2.5. Meteorology and fire behaviour. Wind, temperature and ambient
humidity
- Temperature, relative humidity and local (topographic), storm, mesoscale (breezy,
anabatic and katabatic) and synoptic winds.
2.6. Topography and fire behaviour. Slope, unevenness and aspect of
exposure. Macrotopography and microtopography
- Effects of macrotopography and microtopography on wildland fire behaviour.
Macrotopography: shape and aspect of geographical features, latitude and distance from
the sea. Microtopography: slope, unevenness and aspect of exposure.
2.7. Fuels and fire behaviour. Typology, thickness and compactness.
- Fuel characteristics: typology, thickness and distribution. Typology: live and dead.
Thickness: time lag, dry window or cumulative dry hours and ratio of dead to live.
Distribution or compactness: surface, understory and canopy strata. Spreading strata:
subsoil, surface and canopy. Fuel load.
TEST: Fire behaviour fundamentals.
SEG 1: Operation safety planning and lessons learned
1. Introduction.
1.1. Safety Culture I - Accidents, protocols and human factor
- History and origin of standard firefighting orders and protocols.
2. Operation safety planning
2.1. Safety planning in an PPE, LACES and AWARENESS operation
- PPE, LACES, relation between LACES - fire reading - scenario - operation. Understanding
the scenario and watch-out situations/indicators.
2.2. Safety protocols and last resort operations, self-protection operation
with a fire engine.
- Security protocols. Awarness - Cycle of situational awareness. LACES - its relation to the
Awarness protocol. 10 standard firefighting orders. 18 watch-out situations. Self-protection
operation with a fire engine.
3. Lessons learnt
3.1. Fireshelter, situational awareness, tactical and operational safety
- Lessons learned: testimony of a survivor of a fatal accident in Spain. Recommendations
and situational awareness in operations.
Practical exercise: Situational Awareness and LACES


 Conversations with successful professionals
Conversations with successful professionals Downloadable materials
Downloadable materials Assessment tests
Assessment tests
